Understanding Binaural Beats
Binaural beats are an auditory phenomenon that occurs when two tones of slightly different frequencies are presented separately to each ear. Your brain perceives a third tone that oscillates at the difference between the two frequencies. This effect can be perceived in the frequency range of about 1-30 Hz, which overlaps with human brainwave frequencies. Some research suggests this might influence brain activity, though the evidence is still developing.
The phenomenon was first discovered in 1839 by Heinrich Wilhelm Dove, but it wasn't until the late 20th century that scientists began studying its potential effects. Some research suggests binaural beats might influence cognitive and psychological states, though the evidence is mixed and individual responses vary widely.
Research shows that binaural beats effectiveness varies across brainwave frequency bands. Beta and alpha frequencies tend to show the most consistent benefits for focus and cognitive performance, though individual responses can differ significantly.
The Brainwave Entrainment Hypothesis
The foundation of binaural beats research rests on the brainwave entrainment hypothesis, which suggests that external stimulation at a certain frequency can influence the brain's electrical activity to oscillate at a similar frequency. This concept provides the basis for research on how binaural beat stimulation affects cognitive and emotional states. Recent neuroscientific research has begun to uncover the brain mechanisms underlying this entrainment process.
Personalized binaural beats, specifically those within theta and beta EEG bands, have shown promising results for improving brain entrainment. Research involving 20 healthy volunteers demonstrated that personalized theta and beta binaural beats for 20 minutes produced larger absolute power differences in bilateral temporal and parietal regions compared to resting state. This suggests that individualized approaches to binaural beat therapy may enhance effectiveness.
Frequency-Specific Effects on Cognitive Performance
Different frequencies of binaural beats correspond to distinct brainwave states and cognitive benefits. Research has identified specific effects for each major frequency band, providing a scientific foundation for targeted cognitive enhancement.
Alpha Frequency (8-13 Hz): The Flow State Enhancer
Alpha frequency binaural beats have demonstrated particular effectiveness for enhancing cognitive performance. A comprehensive study involving 31 healthy participants found that 10 Hz binaural beats reduced response time and intrasubject response time variability while improving visuospatial working memory performance. The research showed that alpha-band binaural beat entrainment may have enhancing effects within the visuospatial modality.
Beta Frequency (13-30 Hz): Cognitive Processing Power
Beta frequency binaural beats excel at enhancing complex cognitive tasks. Research with 200 healthy young adults demonstrated that both beta (18 Hz) and gamma (40 Hz) binaural beats yielded better performance compared to baseline, especially for syntactically complex language processing tasks. Studies specifically examining 15 Hz binaural beats found significant improvements in visuospatial working memory, with working memory serving as the foundation for numerous cognitive functions.
Theta Frequency (4-8 Hz): Meditation and Stress Reduction
Theta frequency binaural beats are particularly effective for relaxation and stress management. Research involving traffic noise exposure and binaural beat entrainment found that alpha sub-waves increase after theta binaural beat exposure, while beta sub-waves decrease, indicating a shift toward a more relaxed state. EEG measurements confirm that binaural beats can objectively induce states of relaxation, with effects observable across multiple brain activity metrics.
Gamma Frequency (30-100 Hz): Enhanced Attention and Processing
Gamma frequency binaural beats show promise for enhancing high-level cognitive processing. Studies demonstrate that gamma binaural beats can improve performance on complex language comprehension tasks, particularly those requiring interpretation of syntactic relations. Research indicates that gamma frequencies may enhance auditory sentence comprehension and support advanced cognitive operations.
Click to zoom
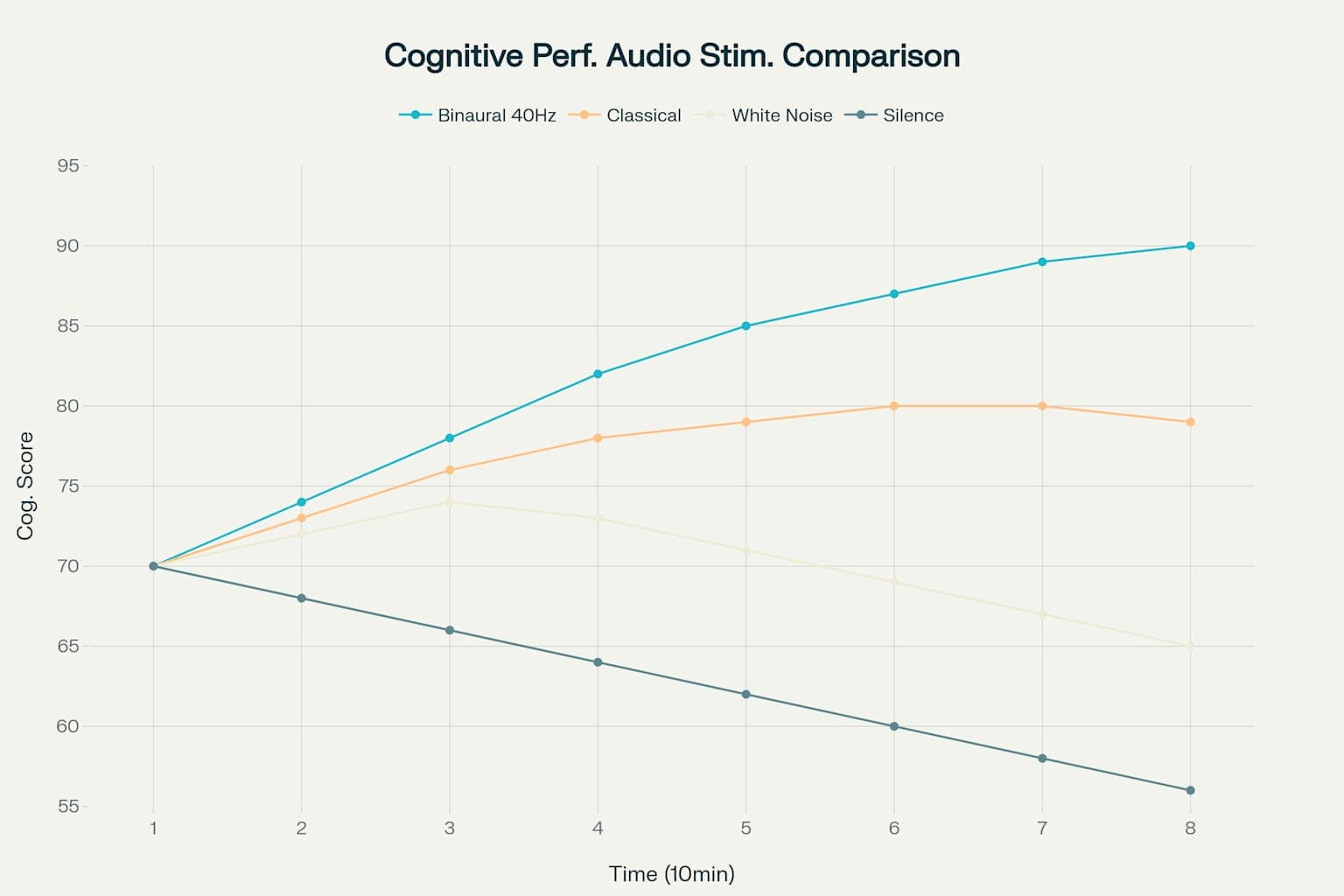
Some research suggests binaural beats may provide cognitive performance benefits during extended focus sessions, with gamma frequency (40Hz) showing particular promise in certain studies. However, results vary between individuals, and more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms.
The Neuroscience Behind Binaural Beat Effects
Modern neuroscience research reveals that binaural beats produce measurable changes in brain activity patterns. Studies using machine learning approaches to predict binaural beat effectiveness have achieved 90% accuracy in identifying individuals who respond positively to binaural beat stimulation. The research identified frontal and parietal EEG channels in theta and alpha bands as crucial for determining binaural beat responsiveness.
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy studies show that personalized soundscapes, including binaural beats, can increase focus significantly above silence. Brain-computer interface technology research involving 62 participants found that engineered soundscapes increased focus, with classical music, engineered soundscapes, and natural sounds proving most effective for focus enhancement.
Practical Applications and Individual Differences
Research consistently shows that individual differences significantly affect binaural beat effectiveness. Studies demonstrate that working memory enhancement through binaural beats varies considerably between individuals, with some people showing dramatic improvements while others experience minimal effects. Machine learning models can now predict individual responsiveness with high accuracy, enabling personalized interventions.
The spatial characteristics of sound appear crucial for binaural beat effectiveness. Research investigating spatially moving sounds found that binaural, panning sounds and alternate beeps had more pronounced effects on electrical brain activity than control conditions. This suggests that the impact of auditory stimulation lies in spatial attributes rather than the sensation of beating itself.
Combining Audio with Focus Tools
Some focus tools combine binaural beats with distraction blocking features. The idea is that blocking distractions removes negative influences on attention, while audio stimulation might provide additional cognitive support. However, research on this combined approach is still emerging, and individual results will vary.
Establishing Best Practices for Binaural Beat Use
Scientific research provides clear guidelines for maximizing binaural beat effectiveness. Studies indicate that 15-20 minute sessions are optimal for cognitive enhancement, with longer sessions potentially producing diminishing returns[14]. The volume should be comfortable and non-intrusive, as excessive volume can actually impair cognitive performance.
1. Match Frequency to Intended Outcome
Research demonstrates frequency-specific effects: use alpha frequencies (8-13 Hz) for flow states and creative work, beta frequencies (13-30 Hz) for analytical tasks and problem-solving, theta frequencies (4-8 Hz) for meditation and stress reduction, and gamma frequencies (30+ Hz) for complex cognitive processing[7][9].
2. Consider Individual Responsiveness
Studies show that approximately 60-70% of individuals respond positively to binaural beats, with effectiveness varying based on individual brain characteristics. Start with shorter sessions to assess personal responsiveness before committing to longer protocols.
3. Use Quality Stereo Headphones
The binaural beat effect requires separate frequency presentation to each ear, making quality stereo headphones essential. Speakers cannot produce the same effect due to acoustic mixing in the environment.
4. Combine with Distraction-Free Environment
Binaural beats work best when you can actually focus on them. Eliminating distractions in your environment can help you get the most out of binaural beat sessions by allowing you to maintain sustained attention.
Finding What Works for You
If you're interested in trying binaural beats, there are several options available. Some services focus specifically on binaural beats, while others combine them with music or ambient sounds. The key is finding what works for your individual needs and preferences.
Keep in mind that research on binaural beats is still evolving, and not everyone responds the same way. Some people find them helpful, while others notice little to no effect. The best approach is to experiment with different frequencies and see what, if anything, works for you.
What We Still Don't Know
Research on binaural beats is ongoing, and there's still much we don't fully understand. Some studies show promising results, while others find minimal effects. Individual differences play a significant role, and what works for one person may not work for another.
The field is exploring personalized approaches based on individual brain characteristics, and future research may help us better understand who benefits most from binaural beats and under what conditions. For now, the best approach is to keep an open mind, try different options, and pay attention to what actually helps you focus.
Binaural beats are an interesting area of research with some promising findings, but they're not a magic solution. If you're curious, it's worth experimenting with them alongside other focus strategies like eliminating distractions, managing your environment, and practicing sustained attention.